 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...Fire Protection in Dust Collectors
Posted on 20th Jul 2023
Fire protection on dust collectors is crucial in industrial settings where dust and other particulate materials are generated and collected. Dust collectors, also known as baghouses or dust filtration systems, are used to remove airborne dust and particulate matter from industrial processes, preventing them from polluting the surrounding environment and posing health risks to workers.
However, certain types of dust can be highly flammable or combustible, and when a sufficient quantity of dust accumulates in the collector or its associated ductwork, it can lead to a potential fire or explosion hazard. Therefore, fire protection measures are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure the safety of personnel and equipment.
Sparks and embers can be generated from various industrial processes and equipment, and if these sparks enter the dust collection system, they can ignite the accumulated dust, potentially leading to a fire or explosion.
Here are some common fire protection features and strategies implemented in dust collectors:
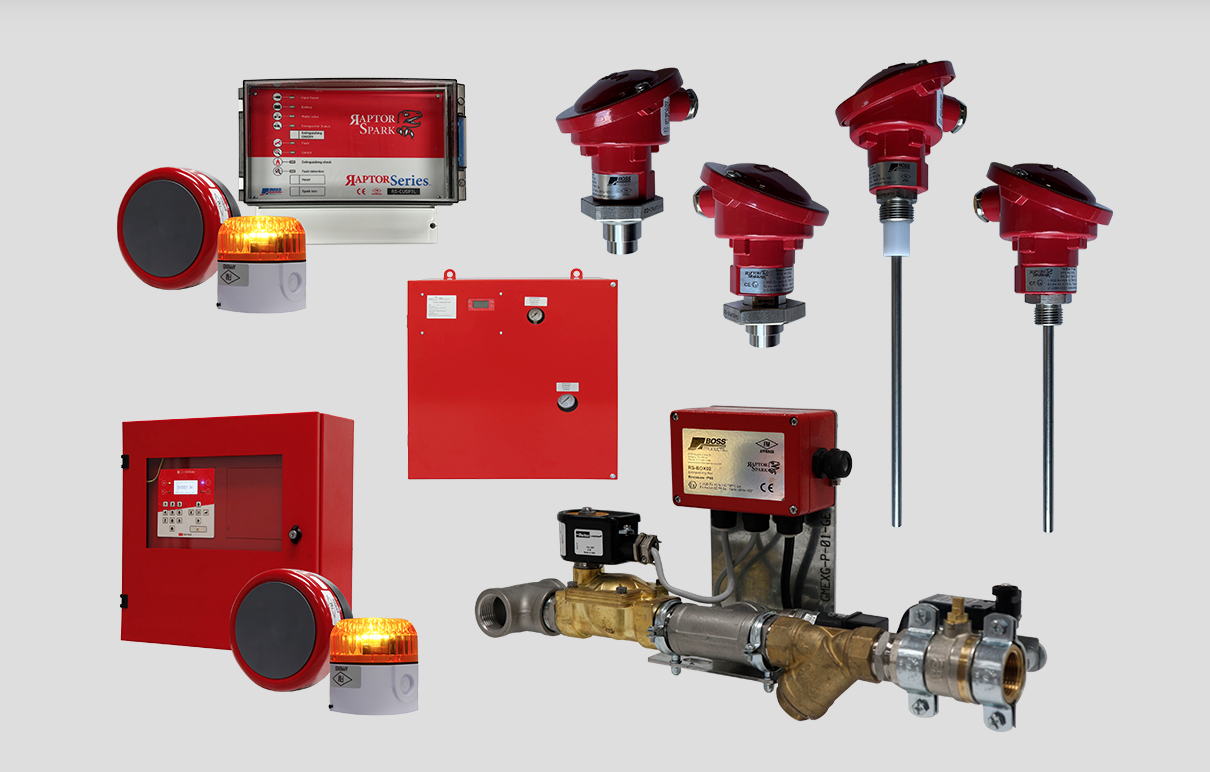
1.Spark Detection and Suppression: Spark detection systems consist of sensors placed at strategic locations in the ductwork or near potential ignition sources. These sensors can detect sparks or flames, and when a spark is detected, the system triggers an automatic suppression mechanism. This mechanism could involve the injection of water or a fire suppressant into the ductwork to extinguish the spark before it reaches the dust collector.
2.Spark Arrestors: Spark arrestors are devices installed in the ductwork that serve as a barrier to prevent sparks from entering the dust collector. They are designed to cool down or extinguish sparks by using various methods, such as deflection, moisture injection, or mesh screens.
3.Spark Trap: A spark trap is a passive device installed in the ductwork. It slows down the airflow, allowing sparks and hot particles to lose their energy and fall into a separate collection container or drop out of the airflow before they can reach the dust collector.
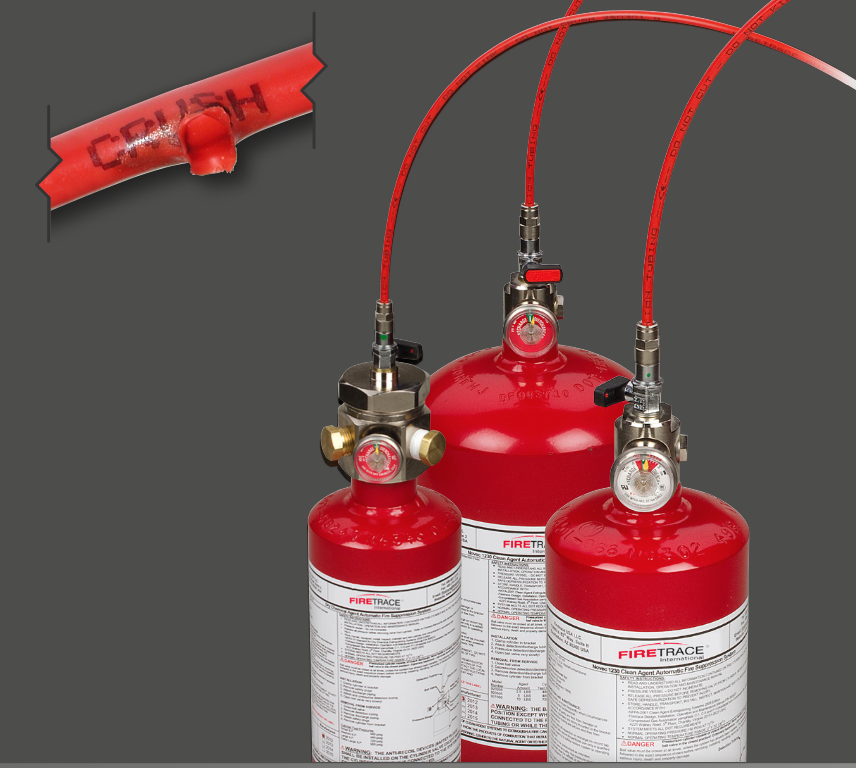
4.Fire Suppression Systems: In addition to spark detection and suppression, some dust collectors may be equipped with automatic fire suppression systems. These systems can use various agents, such as water mist, dry chemicals, or foam, to extinguish fires that may occur inside the dust collector.
5.Inerting Systems: Inerting involves reducing the oxygen concentration inside the dust collector to a level below which combustion cannot occur. This is achieved by injecting inert gases, such as nitrogen or carbon dioxide, into the collector's enclosure or ductwork. Inerting helps prevent fires by eliminating the necessary oxygen for combustion.
6.Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding and bonding of equipment and ductwork are essential to prevent the buildup of static electricity, which can cause sparks and pose a fire hazard. Grounding ensures that any static charges are safely dissipated.
7.Regular Maintenance and Inspection: Proper maintenance and regular inspection of dust collectors are vital to ensure their effective functioning and to identify any potential fire hazards. This includes cleaning the collector, changing filters, and inspecting for damaged or worn-out components that could increase the risk of a fire.
8.Compliance with Codes and Standards: Industries must adhere to relevant codes and standards related to dust collection and fire protection. These regulations, such as those set forth by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), outline specific requirements to ensure the safety of workers and the prevention of fires and explosions.
Overall, fire protection on dust collectors is a multi-faceted approach that combines detection, suppression, spark prevention, grounding to reduce static charges and combined with proper cleaning measures this can greatly minimize the risk of fires and protect workers and equipment in industrial environments dealing with combustible or flammable dust.



