 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...Fume Extraction in Robotic Weld Cells
Posted on 14th Feb 2023
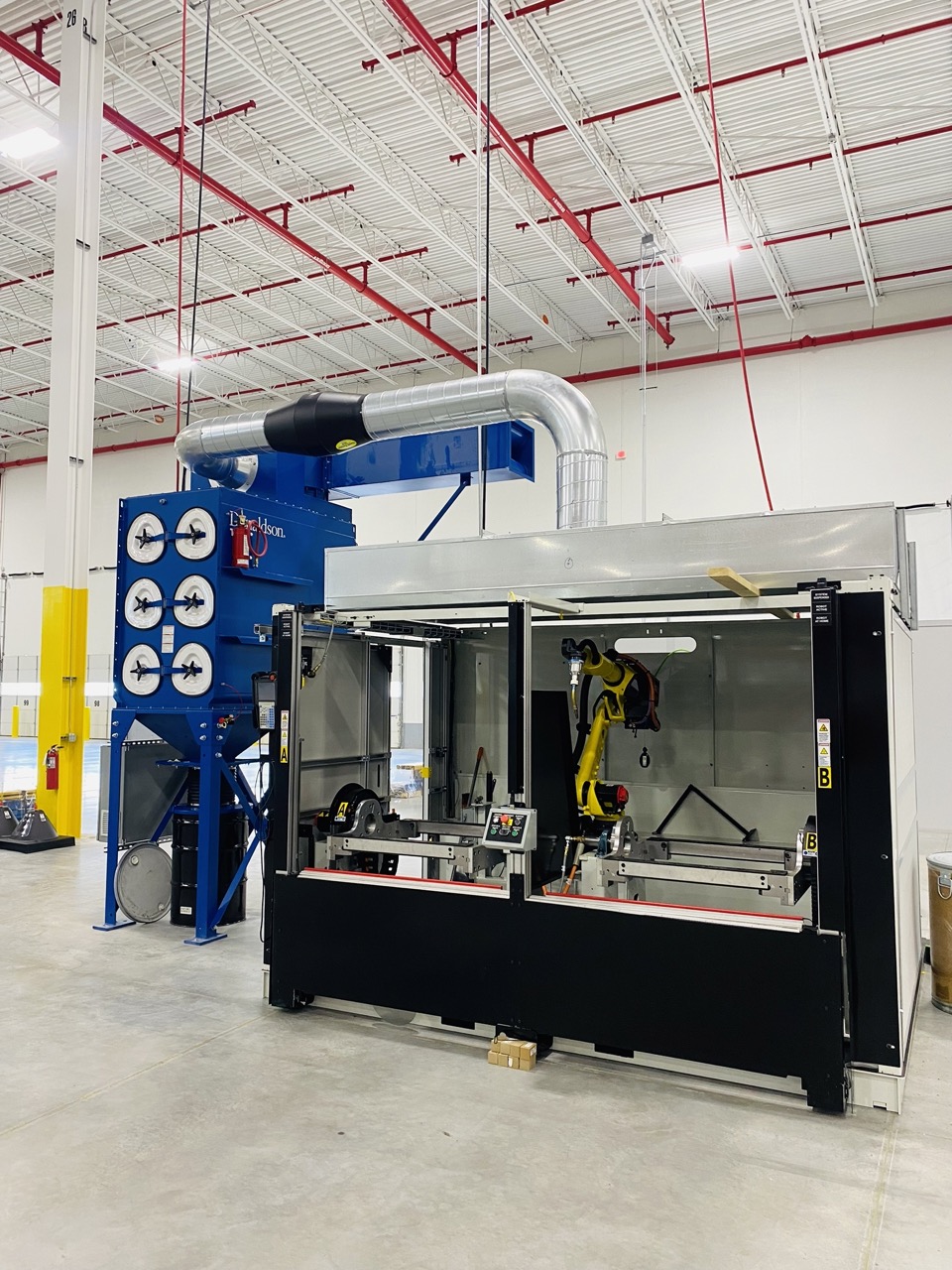

CFM stands for cubic feet per minute, which is a unit of measurement for air flow rate. CFM is a commonly used term in dust, mist and fume collection design and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) and other applications where air movement is important.
To calculate CFM, you will need to know two key values: the volume of air you need to move, and the speed at which you need to move it.
Here's a simple formula for calculating CFM in a robotic welding cell:
CFM = (Volume of Air) * (Air Changes per Minute) / 60
Where:
- Volume of Air is the total volume of air in the space you're trying to evacuate welding smoke/fume, usually measured in cubic feet.
- Air Changes per Minute (ACM) is the number of times per minute you want to completely replace the air in the space.
For example, if you have a welding cell that is 10 feet long, 10 feet wide, and 8 feet tall (for a total volume of 800 cubic feet), and you want to change the air in the cell twenty times per hour or every 3 minutes, your calculation would be:
CFM = (800) * (20 / 60) = 266 CFM
This means you need an air flow rate of 266 cubic feet per minute to completely change the air in the cell every three minutes.
Duct engineering, AMR (air to filter media ratio) and blower design would then be completed to ensure that originally designed CFM is accomplished with a new fume collector system or exhaust fan.
It's important to note that this is a simple example, and the actual CFM required for a given space will depend on a variety of factors, such as the size and shape of the cell, quantity of louvers or openings in the booth/cell, the volume of robotic production, the type of ventilation system or fume collector being used, and other considerations. It's always best to consult with a professional engineer at PCS for a more accurate assessment of your ventilation needs.
